Technical SEO: I am sure your first reaction to the term technical SEO is not a good one. From my experience, unless I am talking to an IT person or a web developer, people typically get nervous when they hear the word technical. In this case, it just refers to all of the work done from an SEO perspective that is not directly related to content.
This aspect of SEO is concerned with how well search engine spiders can crawl your site and index your content. In my opinion, it is the foundational component of SEO. It should be the first part of your SEO project plan. It makes little sense to write new content and optimize current content before the technical SEO on your website has been addressed.
Let’s go over a few examples of technical SEO.
Speed!

Google uses site speed and load time as a ranking factor. There are a number of issues that can affect the speed of your site. Before you troubleshoot technical issues on the actual website that can be slowing down your site, take a good hard look at your hosting. The $6 a month hosting plan can be tempting, but it will inevitably slow your site down and cost you big bucks in the long run. Find a plan that will ensure your site is fast and will provide a good experience for visitors.
You can also speed up your site by using a content delivery network (CDN), setting up browser caching, compressing images, minimizing the use of plugins, and getting rid of render-blocking JavaScript or CSS above the fold.
Is your site mobile friendly?
Remember mobilegeddon, Google’s algorithm update that punished non-mobile-friendly sites. In the fall of 2014, comScore published a report highlighting that mobile became the leading digital platform. Having a mobile-friendly site is critical to a sound technical SEO strategy and to keep bounce rates to a minimum.
Thankfully, there are many tools available to check the mobile-friendliness of your site. Google recently released a tool that checks both speed and mobile optimization. Be sure to test your site, and request the free report from Google. If you receive a substandard score, the report identifies exactly what needs to be fixed. This information can be perfect to send to your developer.
I am really only scratching the surface on technical SEO. My goal is to give you a high-level overview on a few key areas. Other aspects that would fall under technical SEO include your site’s architecture, your HTML and XML sitemaps, getting rid of crawl errors (you can identify them in the Google Search Console), setting up redirects properly, and using schemas in your website.
Once you have completed an audit of your technical SEO infrastructure, it’s time to move on to on-page SEO.
For a detailed write up of Technical SEO, check out my blog post, Technical SEO | 20 SEO Tips for your Website.
On-Page SEO: This type of SEO is concerned with the content on your website and how well it is optimized for targeted and relevant keywords. Think of on-page SEO as the content components that provide a good or bad user experience for site visitors. Is the content well written, unique, and relevant to what the visitor is looking for? Or is the content poorly written, full of duplicate messaging, and inconsistent with what information the site visitor was seeking.
Off-Page SEO: This type of SEO refers to the strategies you implement outside of your website that can influence your rankings. Many site owners think their SEO work is complete once they have addressed technical concerns and optimized all of their pages. Not true at all! There are many necessary Off-page SEO factors that can have a meaningful impact on your organic rankings.
Let’s take a look at a few Off-page SEO strategies.
Link Building!
Link building is the most important off-page factor. This is the process of getting external links from pages of other websites to link to your site. These links show Google that your content is popular and is being shared. Not all links are equal, though. A link from a large authoritative publisher will carry much more weight than a link from a site with barely any traffic.
The truth is, I could easily write a 5,000-word article covering all of the different link building strategies. There is an abundant amount of tactics that smart marketers use to link build. But I can tell you this, all of them start with having great content. The better your content is, the more likely external sites will be willing to give you a backlink.
Social Bookmarking
This is the process of saving favorite websites and favorite pages using a social bookmarking site. Popular social bookmarking sites are Digg, Delicious, Reddit and StumbleUpon. Typically, social bookmark services include user-generated tags relating to website content. In many cases, users can vote or comment on bookmarked items. If your site or a certain page becomes popular, you can see a nice uptick in traffic. That is really just touching lightly on off-page, but now you know the difference of all three types of SEO.
A Perfectly Optimized Page
In this article, I am going to cover the details of what I determine to be a perfectly optimized page for on-page SEO.
- Title Tags!
This is the most important on-page SEO factor. Title tags are used on search engine results pages to provide a preview for a specific page. Think about the importance of the copy when writing title tags. To me, it is essentially like writing text ad copy for a pay-per-click ad. The more engaging the copy, the higher the click-through-rates will be.
Make sure you start the title with your keyword or place it as close to the beginning as possible. Notice my title tag for this page starts with “On-Page SEO.” The closer your keyword is to the beginning of the title tag, the better it will be for search engines.
If you have a subheading, consider wrapping it in an H2 tag. This is not as important as the H1 tag, but it is another way to optimize your page. Plus, if your niche is really competitive, you will need to go above and beyond and get all the SEO juice you can.
- Use Clean and Easy-to-Read URLs
This is one of the easiest and least time-consuming SEO tactics. The key thing to avoid is allowing your content management system to pick the URL on your behalf. This can result in random URLs that are not friendly to search engines and are off-putting to site visitors.
For example, consider the URL www.rocketpliots/SEO/default.asp?sid=9DF4B. Why not spend a few seconds to change the URL to something more friendly like https://rocketpilots.com/sandiegoseocompany. It’s easy on the eyes and relevant to the content of the page.
- Use Modifiers in Your Title
By now, you are probably familiar with keyword research tools like Goolge’s Keyword Planner, Spyfu, SEMrush, and keyword tool. One thing all of these tools have in common is that they do a great job of identifying long-tail keywords—especially long-tail keywords that contain five to eight words. Long-tail keywords are specific searches with three or more words that users typically use when they are closer to a purchase. Since the user is closer to making a buying decision, you don’t want to miss out on this traffic.
A great way to optimize your page for long-tail keywords is to add modifiers to the title of your page. The following are examples of modifiers:
- the current year, like “2016”
- “best”
- “review”
- “guide”
- “checklist”
- “template”
- “case study”
Add modifiers and ensure that you are capturing long-tail keyword traffic and not missing out on prospects that are ready to convert to customers.
- Make Sure Your Blog Post Has Only One H1 Tag
Some WordPress themes and other Content Managements Systems will automatically wrap your blog post title in an H1 tag. But, it’s very important to makes sure this is the case with your specific theme.
It’s very easy to check your site’s code or have your webmaster take a look. An H1 tag will increase the text size. So, sometimes a WordPress theme will wrap other prominent text in an H1 tag in order to increase the font size. Bottom line, you want to make sure your page only has one H1 tag and that it includes your keyword.
If your theme does this automatically every time you add a new post, you’re in great shape. If it creates two H1 tags, you will have to spend the time to go in and remove the second H1 tag.
- Use Pictures, Charts, Videos, and Infographics

Producing basic content exclusively with text is no longer enough to keep your readers’ attention. Not only should your content, especially blog postings, be 1,000 to 3,000 words, but it must also be paired with engaging multimedia. Sometimes website traffic can be a vanity metric. For example, if you are receiving an increased amount of traffic each month, that is only good if the traffic is converting, interacting with your content, sharing your content, linking to your content, and staying on your site for an extended period of time.
Google pays attention to user interaction signals, time on site, and, of course, backlinks. So, don’t just focus on text, but enhance the user experience by including awesome pictures, visualizations, and videos. Going the extra mile will surely pay off when your brand is followed by a group of loyal blog readers and devoted customers.
- Use Your Keyword Early
I have noticed that people are starting to write longer articles, pages, and blogs. As a consequence, the preface to the content is becoming voluminous, and sometimes the targeted keyword isn’t mentioned for a few hundred words. This is bad news!
It’s important to include your keyword within in the first 100 words. Don’t overthink this concept. If you’ve carefully selected a keyword to target and your write up is relevant to the keyword, then this will probably happen naturally. Don’t place the keyword into an unnatural spot. Just remember to use it early in an effort to help Google and your site visitors understand what your article is all about.
- Make Sure Your Site is Mobile-Friendly
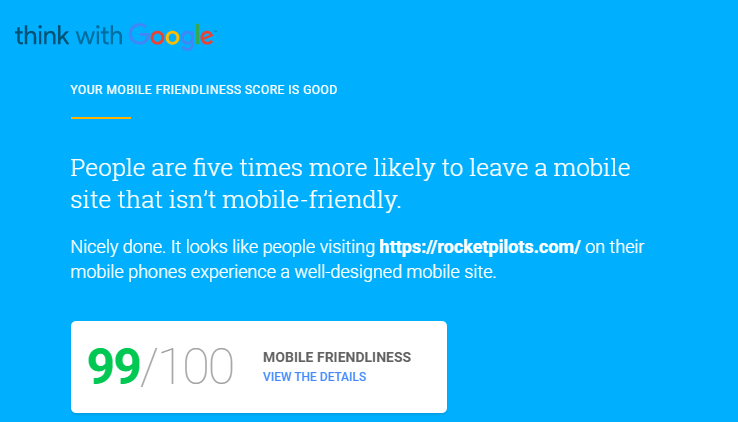
Here is where there is a little crossover between technical SEO and on-page SEO. Earlier in this article I covered the importance of a mobile-friendly site and categorized the work under technical SEO.
The thing is, you can’t have a perfectly optimized page if your site is not mobile-friendly. Make sure your site is optimized for mobile devices so your pages are outranking your competitors on mobile searches. Reference Google’s Mobile SEO Overview for details.
- Incorporate Outbound Links
As you’ve been reading this article, have you noticed the outbound links sprinkled throughout? This is a really easy SEO strategy to implement. It helps search engines understand your content better and also helps provide examples to your readers.
Outbound links that supplement your content help search engines determine what your article is about and ultimately affect your rankings. Of course, you need to be selective when using outbound links. Link to sites that are of high quality, are relevant to your article, and will provide a good experience for your site visitors.
Here’s a perfect example. I am writing an article about the importance of including relevant outbound links in your content to help rank your site. I’m going to link to an authoritative website about a Study That Shows Outgoing Links Have a Positive Effect on SEO.
- Use Internal Links
This is definitely one of my favorite SEO tactics because it promotes linking to our own content! For example, you are currently learning about the different types of SEO and how to create the perfectly optimized page. When you are interviewing an SEO company, you will be well equipped to interview them on how they will optimize your website pages. Trust me when I tell you, you are now far ahead of most of the other business owners out here. Check out my previous posting for more tips on How to Interview a SEO company for your San Diego Business. See how I did that? Just a simple link to a previous blog posting that is relevant to this article and my example.
For more examples, check out almost any Wikipedia article. They include an abundance of keyword-rich internal links. Now, they are Wikipedia so it’s acceptable for them to have over fifty links per write-up. But, typically I would recommend about four internal links per posting. One or two internal links for every 1,000 words is a good rule of thumb. Happy linking!
- Use LSI Keywords
Here is one you may not have heard of: LSI stands for Latent Semantic Indexing. Put another way, these are words that are semantically related to your keywords. You’re probably wondering why I didn’t just say synonyms. That’s because there are semantically related words that don’t necessarily fall under the category of synonyms.
Let’s discuss LSI keywords in practice. If you are committed to writing long content, you don’t have to put much thought into using LSI keywords. An innate characteristic of long postings is the natural usage of LSI keywords.
If your postings will be shorter, there are a few tools you can use to identify LSI keywords. When you conduct a Google search, at the very bottom of the page, there will be a section titled “Searches related to [keyword].”
Consider incorporating some of these keywords into your posting.
You can also use LSIGraph for free. Just type in your keyword and click generate to receive a list of LSI keywords. Use these keywords throughout your posting and you’re well on your way to a perfectly optimized page.
- Optimize Your Images
This is a really easy one that should simply become a best practice every time you save an image and write the text for the Alt tag.
First, when you save your image, include the keyword in the file name. If you buy an image from Getty Images, iStock, or Shutterstock, all you have do is save the file with your target keyword. For example, “On_Page_SEO.jpeg.”
When you upload the image, don’t leave the text for the Alt tag blank. Simply include your keyword in the Alt tag. One way to standardize on the process is to set the Alt tag to be the same name as the image.
You probably won’t get much traffic from Google image searches, but another advantage to optimizing your images is giving your pictures the chance to show up in Google image search results.
You will also want to compress your images for speed. Make sure to use a tool like compressjpeg or the sprite pad developed by Kissmetrics.
- Make Sharing Easy
We all know that backlinking is one of the most important ranking factors when it comes to SEO. I like to give myself every chance possible to receive a high quality backlink. One indirect way to receive an unexpected backlink is having your content shared on social media.
People definitely share informative and insightful content, but they won’t always go out of their way to share content. It’s your job to make sharing the content as easy as possible. Make sure it’s easy for visitors to share your content on Facebook, Twitter, and Google+. If someone with a large social media audience shares your content, it could result in a site owner adding the link to their site and giving you a backlink, or it could result in an increase in brand exposure and new traffic from social media.
- Long and Fantastic Content
It’s now a fact of life that long content ranks better than shorter postings. But, lengthy content is not enough. Search engines want long content that provides unique value to your site visitors. For your content to fall into this category, you will have to spend a considerable amount of time conducting research, writing, sourcing multimedia, wordsmithing, and constructing a posting that is best in its class!
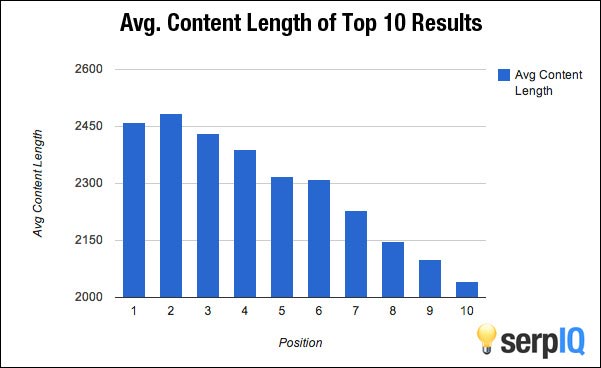
The graph from serpIQ tells us that the first ten results are typically from content-rich sites. The days of quickly pumping out postings of 300 to 400 words and getting rankings are over. I normally advise businesses to write at least 1,000 words per new article. But, to produce a killer posting that will be full of interactive content that will keep your users coming back, you should really strive for 2,000 words or more.
- Meta Descriptions
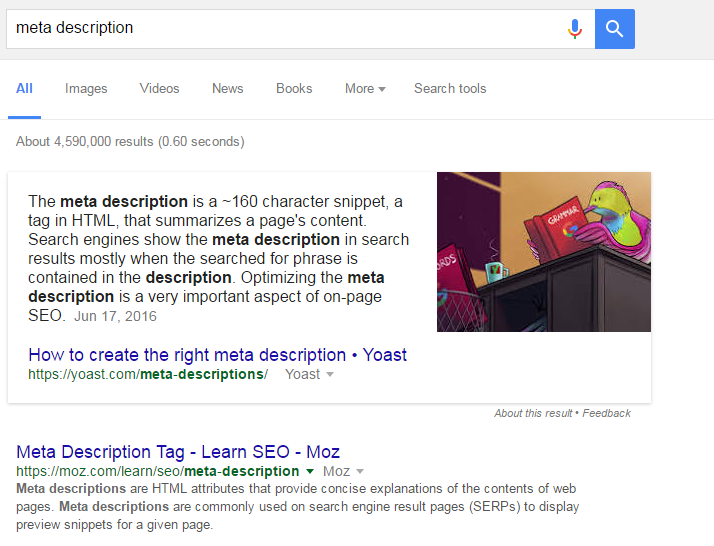
I really wish we had a different name for this character snippet. Meta description sounds so technical, and I typically receive a blank stare when I use this term in front of a prospective client.
A meta description is a 160-character summarization of the page’s content. It’s an HTML attribute that succinctly explains the contents of a web page.
Meta descriptions are shown on search engine results pages as a preview to the webpage’s content. The keyword from the search query is often in bold if it is included in the meta description.
Search engines use meta descriptions to determine what topic you are writing about and which audience they should send to that site. So make sure it’s thoughtfully written and descriptive, yet concise.
Think about your organic click-through-rate when writing your meta descriptions. Search engines use organic click-through-rates in their algorithm to rank websites. So make sure your meta descriptions are persuasive and relevant.
Conclusion
My goal for this in-depth article was to give you a guide to follow for your on-page SEO. Bookmark this link, share it with your webmaster, or use it as a discussion point with your SEO provider. I hope the tactics outlined in this article will serve as a checklist for your business when optimizing your pages.
Remember to get your site ready for all of the fantastic content you are going to produce on a regular basis. A strong foundation is the cornerstone to every SEO strategy. Too many marketers overlook the basics and just start producing content and going after inbound links.
Incorporate all of the tactics into your process and remember that SEO is a discipline. Everyone always wants quick results, but if you create good SEO habits, in the long run the results will follow. Lastly, while it’s important to appease search engines, it’s also critical to keep your site visitors’ experience in mind. Keep your visitors happy and feed them the information they are looking for, and your site will be rewarded with a steady increase in quality traffic that converts.
I own a San Diego SEO company and would love to help you optimize your websites pages. Check out my SEO Services and call me today for your no obligation quote.
Email brian@rocketpilots.com call me today at 858-775-4110 or request a no commitment consultation.
Are you implementing any of these on page SEO tactics on your website? Share your experiences in the comments below. We would love to hear from you!
Brian Hansen